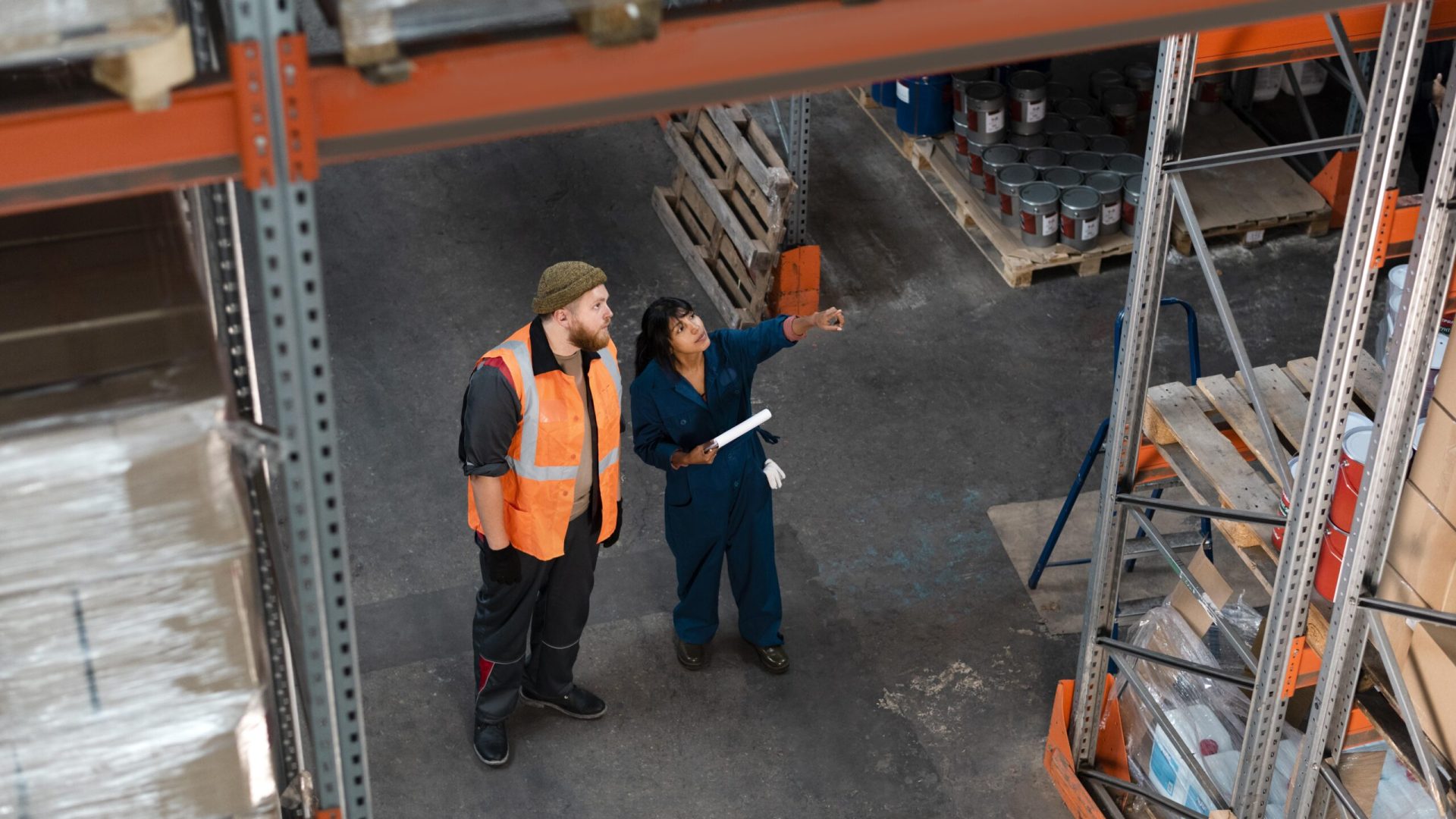
Optimizing Logistics: The Role of Yard Management and Transport Management Systems
Efficient logistics and supply chain operations hinge on the effective coordination of multiple components, among which yard management (YM) plays a pivotal role. Yard management refers to the administration and control of trucks, trailers, and containers as they arrive, dwell, and depart from a warehouse or distribution center. From a transport management system (TMS) perspective, yard management is integral to optimizing transportation operations, reducing costs, and enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
The Role of Yard Management
Yard management is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures the seamless flow of goods into and out of a warehouse, thus minimizing congestion and delays. Effective yard management involves tracking the location of trailers, monitoring the status of each vehicle, and coordinating the movement of goods to and from loading docks. This coordination is vital for maintaining operational efficiency and meeting delivery schedules.
Secondly, yard management helps in maintaining safety and security. By keeping track of all vehicles and their contents, it minimizes the risk of theft and ensures compliance with safety regulations. Properly managed yards can also prevent accidents by organizing the movement of vehicles and personnel within the yard.
Lastly, yard management contributes to cost savings. By reducing idle times for trucks and trailers, it lowers detention fees and enhances asset utilization. Improved yard operations can lead to better labor management, as workers can be scheduled more effectively to match the flow of goods and vehicles.
Transport Management Systems and Yard Management
Transport Management Systems (TMS) are designed to optimize the planning, execution, and monitoring of transportation activities. From a TMS perspective, yard management is not an isolated activity but an integral component of a holistic transportation strategy. The synergy between TMS and YM can be understood through several key aspects:
- Integration and Data Flow: A TMS that integrates yard management features can provide real-time visibility into yard activities. This integration allows for seamless data flow between the transportation and yard management functions. For instance, when a truck is en route to a warehouse, the TMS can notify the yard management system, allowing it to prepare for the truck’s arrival. This real-time data exchange reduces wait times and improves scheduling accuracy.
- Enhanced Visibility: TMS-enhanced yard management provides greater visibility into yard operations. Managers can track the status of shipments and the location of trailers within the yard, enabling better decision-making. This visibility extends beyond the yard, as TMS can provide insights into the entire transportation network, facilitating proactive management of delays and disruptions.
- Optimization and Efficiency: A TMS can leverage advanced algorithms to optimize yard operations. For example, it can schedule dock assignments based on real-time data about trailer arrivals and departures, load priorities, and labor availability. This optimization reduces bottlenecks and ensures that resources are used efficiently.
- Automation and Innovation: Automation is a key benefit of integrating TMS with yard management. Automated gate check-ins and check-outs, real-time yard asset tracking, and automated alerts for delays or issues enhance operational efficiency. Innovations such as IoT devices and AI can further augment yard management by providing predictive insights and advanced analytics, allowing for even more precise control and optimization.
- Performance Monitoring and Reporting: TMS provides comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities that are invaluable for yard management. By analyzing data on yard operations, managers can identify trends, pinpoint inefficiencies, and implement continuous improvement initiatives. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as truck turn time, yard capacity utilization, and on-time performance can be tracked and optimized.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its benefits, integrating TMS with yard management poses certain challenges. The complexity of real-time data integration, the need for consistent data standards, and the potential high cost of implementing advanced technologies can be significant barriers. Additionally, change management is critical, as personnel must adapt to new systems and processes.
Security and data privacy are also crucial considerations. As yard management systems collect and process large amounts of data, safeguarding this information against cyber threats is paramount. Ensuring that all data exchanges between TMS and yard management systems are secure is essential to maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of sensitive information.
Conclusion
Yard management is a critical component of modern logistics and supply chain operations. From a transport management system perspective, effective yard management enhances visibility, efficiency, and optimization of transportation activities. The integration of TMS and yard management systems represents a powerful synergy that can drive significant operational improvements and cost savings. However, to fully realize these benefits, organizations must address integration challenges, invest in the necessary technologies, and ensure robust security measures. As logistics continue to evolve, the role of TMS in enhancing yard management will only grow in importance, underscoring its vital role in achieving seamless and efficient supply chain operations.